Dementia isn’t an age-related condition, but age is a significant risk factor. Drug use can also increase your risk of dementia. Long-term use of benzodiazepines, anticholinergics, and opioids can increase the risk of dementia.
While these drugs have specific purposes or benefits, they can also have side effects. Understanding how these drugs impact cognitive health can help healthcare professionals and adult children or caregivers better care for and make informed decisions that could significantly affect the well-being of loved ones.
We explore which drugs are commonly associated with an increased risk of dementia and practical tips on how to manage medications and make healthy lifestyle choices to mitigate these risks.
What Is Dementia?
Dementia is not a single disease but a broad term encompassing various conditions that impair cognitive function. Dementia affects memory, thinking, language, judgment, and behavior. The most common types of dementia include Alzheimer’s disease. Other types of dementia include vascular dementia, Lewy body dementia, and frontotemporal dementia.
The Impact of Dementia
Living with dementia can be challenging. As dementia progresses, it can affect a loved one’s ability to carry out routine everyday tasks. By learning more about dementia, we can take proactive steps to support loved ones affected by this condition and potentially reduce its onset through informed choices.
Can Drug Use Cause Dementia
Certain drugs can negatively impact the brain and how the brain cells function, leading to cognitive impairment. These substances can alter brain chemistry and impaired functions, such as memory, attention, and problem-solving. It’s crucial to recognize the potential risks associated with drug use to protect the cognitive well-being of individuals.
Common Drugs Linked to Dementia Risks
Several types of drugs have been linked to an increased risk of developing dementia.
Anticholinergics
These include medications for allergies and colds, depression, bladder control, and high blood pressure. Examples of these drugs include antihistamines, tricyclic antidepressants, irritable bowel syndrome medications, and overactive bladder medication.
These drugs can cause brain cell death and poor mental functioning. Long-term use of an anticholinergic, 3 years or more, is associated with a 54% higher dementia risk than 3 months or less of the same dose.
Benzodiazepines
These drugs often prescribed for anxiety and sleep disorders can include anxiety medications and sleeping pills. Side effects of these drugs can include breathing problems, confusion, drowsiness, and problems with cognition. Higher doses over extended periods can increase the risk of impaired brain functioning.
Opioids
Painkillers or opioid pain medications can increase dementia risk when used excessively or improperly and long-term. Chronic pain and the use of these drugs can increase the risk of developing dementia. However, the mechanism is unclear and requires more research.
Examples of opioids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs include:
- Morphine
- Hydrocodone
- Fentanyl
- Naproxen
- Ibuprofen
Managing Medications & Cognitive Health
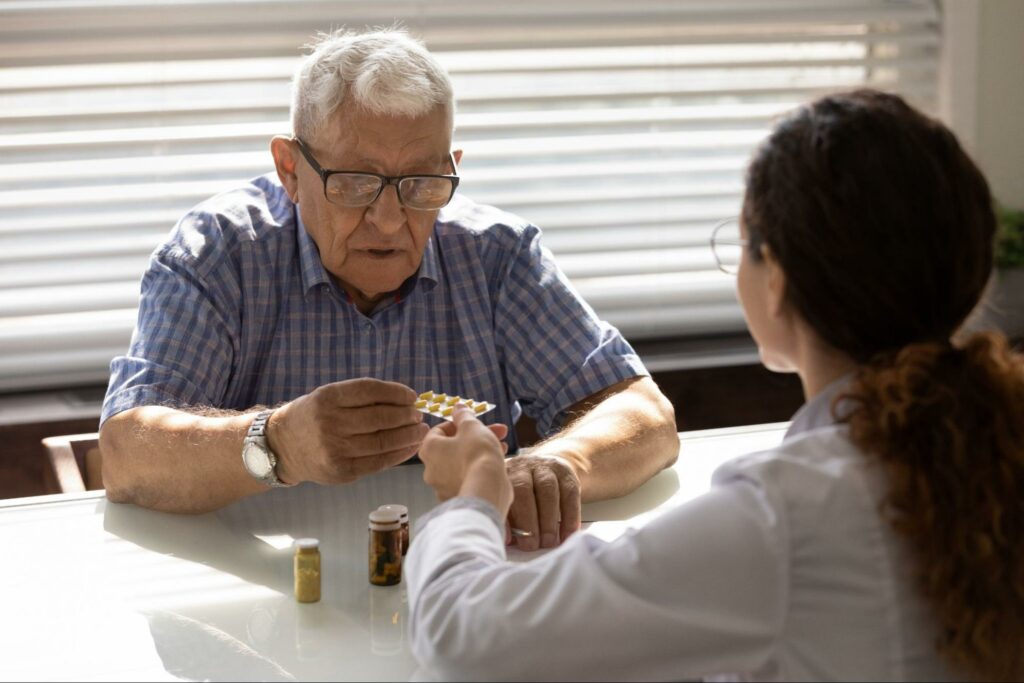

Managing medications includes safe medication practices for reducing dementia risks. Here are some practices to follow before taking medications:
- Consult healthcare providers: Always discuss your medications with your doctor, especially if you’re concerned about their cognitive effects.
- Read prescription labels: Understand dosages, potential side effects, and interactions with other drugs.
- Organize medications: Use pill organizers and set reminders for proper medication administration.
Communication is Key
Adult children and caregivers can help loved ones by effectively communicating with healthcare providers about medication concerns. Older adults should not hesitate to ask questions, seek second opinions, or request alternative treatments.
Monitoring Cognitive Health
Regular cognitive assessments can help track changes and identify early signs of dementia. Share any concerns with your healthcare provider, and consider involving family members or caregivers in monitoring cognitive health.
Dementia Prevention
A healthy lifestyle plays a crucial role in reducing the risk of dementia:
- Balanced diet: Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Regular exercise: Engage in physical activities such as walking, swimming, or yoga.
- Mental stimulation: Keep your brain active with puzzles, reading, and learning new skills.
- Stay socially active: Engage in social activities and maintain connections with friends and family.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol: These habits can harm brain health. If you smoke, seek support to quit and limit alcohol consumption.
- Prioritize sleep: Aim for 7 to 8 hours of quality sleep each night.
Memory Care to Support Loved Ones
Understanding the connection between drug use and dementia risk is vital for safeguarding cognitive health. Knowing the risks associated with certain drugs, managing medications responsibly, and adopting a healthy lifestyle can positively impact older adults’ well-being.
If you have concerns about dementia risk in a loved one or need guidance on medication management, contact Inspired Living at Hidden Lakes for support and professional help. Our memory care program offers various personal care services to help loved ones thrive.